How To Update A Table Based On A Selection Javascript
This tutorial uses jQuery and Bootstrap.
If you are building an app that handles extensive data, yous might want to implement realtime tables at some indicate. Let'south take a content management arrangement for case. Big amounts of data are added and removed oft, and we would like the changes to be available to consumers immediately.
In this tutorial, we are going to walk through implementing similar features on our realtime table. We volition be using a few developer tools, which are:
-
jQuery: A minor JavaScript library rich in features that enable easier DOM manipulation, event handling, animation and AJAX implementations.
-
Pusher Channels: A free realtime, easy to utilize pub/sub service. Channels makes realtime every bit easy every bit using basic events.
-
DataTables: A jQuery plug-in that employs progressive enhancement concepts to add advanced interaction controls to any HTML table.
-
Bootstrap: A front stop framework for developing responsive, mobile kickoff projects on the spider web
Here is a glimpse of what nosotros are going to build:
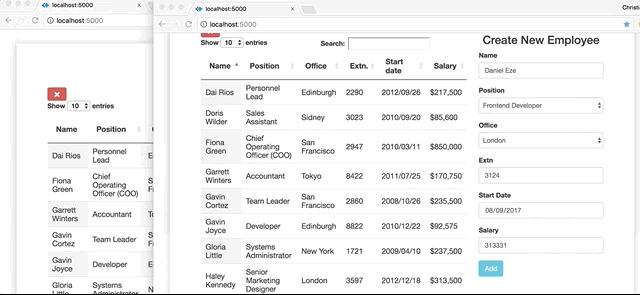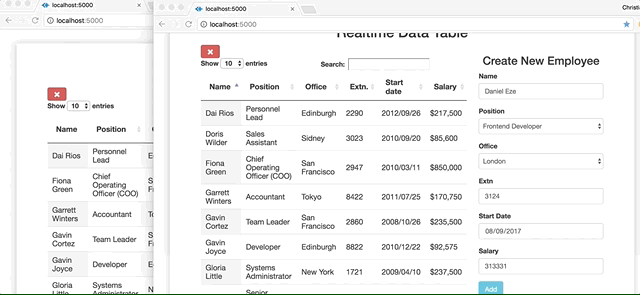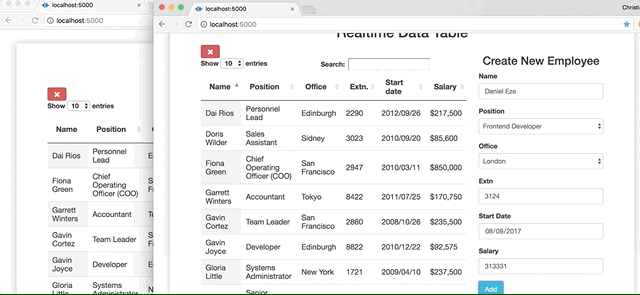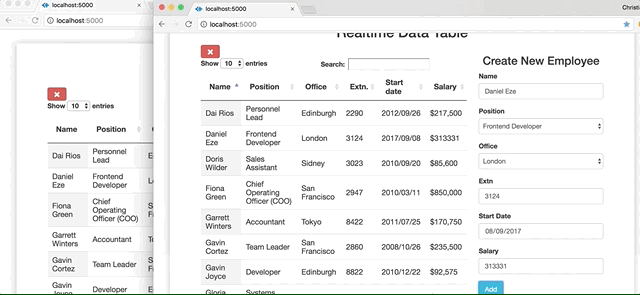
Setting up DataTables
Running DataTables on our app is quite simple and straightforward. All nosotros demand to do is include the DataTables JavaScript file and the DataTables CSS file in our HTML page. There are a host of other plug-ins we can add to heighten editing abilities and extend the feature ready of DataTables but basically we shall stick to these two files. It must be noted that being a jQuery plug-in, DataTables volition rely on jQuery in guild to piece of work. To include DataTables on our page, we but include the following links on our HTML page:
<head > <link rel = "stylesheet" type = "text/css" href = "//cdn.datatables.net/1.10.15/css/jquery.dataTables.css" > </caput > These links volition be at the stop of our <trunk> element, just before its closing tag:
<torso > <script src = "https://lawmaking.jquery.com/jquery-1.12.4.js" > </script > <script type = "text/javascript" charset = "utf8" src = "//cdn.datatables.net/1.x.fifteen/js/jquery.dataTables.js" > </script > <script src = "https://cdn.datatables.net/plug-ins/1.x.xv/api/row().show().js" > </script > </body > Creating our tabular array pattern
To create our table blueprint, we insert a tabular array chemical element in our page and, with jQuery, append the DataTable method to it. This will initialize all the built-in features of DataTables. The DataTable method takes an object as statement. The object has a data property which takes [dataSet](https://github.com/christiannwamba/pusher-realtime-jquery-datatable/hulk/master/information.js) , an assortment of data that nosotros intend to display on the tabular array. Nosotros also include some other belongings called columns and set its value to an array of objects with each object'southward value serving every bit a column header for our table.
const dataTable = $ ( '#realtime' ) . DataTable ( { data: dataSet, columns: [ { championship: 'Proper name' } , { championship: 'Position' } , { title: 'Office' } , { title: 'Extn.' } , { title: 'Kickoff date' } , { title: 'Salary' } ] } ) ; The data set is stored in a different JavaScript file and should be imported earlier the above custom JS file:
<script src= "information.js" > < /script> <script src= "script.js" > < /script> Adding new records to the table
To add new records to our table, we kickoff create a form with valid options in our HTML page. Nosotros so continue to create a method called buildForm() in our JavaScript file. Using jQuery, we make buildForm() return the value of every selection in our form below.
<div course = "col-md-4 col-dr.-offset-1" > <h3 class = "text-center" > Create New Employee </h3 > <div class = "form-group" > <label for = "name" > Name </label > <input type = "text" name = "name" id = "proper name" placeholder = "Proper name" class = "form-control" > </div > <div class = "course-group" > <label for = "position" > Position </label > <select proper noun = "position" id = "position" course = "form-control" > <option value = " " > --Select Position-- </option > <pick value = "Frontend Developer" > Frontend Programmer </option > <option value = "UI/UX Engineer" > UI/UX Engineer </option > <selection value = "iOS Engineer" > iOS Engineer </option > <pick value = "Android Developer" > Android Developer </option > </select > </div > <div class = "course-grouping" > <label for = "office" > Part </characterization > <select name = "function" id = "office" class = "form-control" > <option value = " " > --Select Function-- </option > <selection value = "Lagos" > Lagos </option > <option value = "London" > London </option > <pick value = "New York" > New York </option > <option value = "Berlin" > Berlin </choice > </select > </div > <div class = "form-group" > <label for = "extn" > Extn </characterization > <input type = "number" name = "extn" id = "extn" placeholder = "Extn" grade = "form-command" > </div > <div form = "class-group" > <label for = "startDate" > Offset Engagement </characterization > <input type = "date" proper name = "startDate" id = "startDate" placeholder = "Start Date" class = "form-control" > </div > <div class = "form-group" > <label for = "salary" > Salary </label > <input type = "number" name = "salary" id = "salary" placeholder = "Salary" class = "form-control" > </div > <div class = "course-group" > <push button class = "btn btn-info" id = "add" > Add </button > </div > </div > We then continue to create our buildForm() method:
buildForm ( ) { return [ $ ( '#name' ) . val ( ) , $ ( '#position' ) . val ( ) , $ ( '#part' ) . val ( ) , $ ( '#extn' ) . val ( ) , $ ( '#startDate' ) . val ( ) . replace ( new RegExp ( '-' , 'g' ) , '/' ) , ` $ ${ $ ( '#bacon' ) . val ( ) } ` ] ; } , Nosotros create a method chosen addRow() to append whatever data buildForm() returns.
addRow ( dataTable ) { const formData = this . buildForm ( ) ; const addedRow = dataTable.row. add (formData) . draw ( ) ; addedRow. evidence ( ) . draw ( false ) ; const addedRowNode = addedRow. node ( ) ; console. log (addedRowNode) ; $ (addedRowNode) . addClass ( 'highlight' ) ; } The methods row.add together() and .depict() are inbuilt DataTables API methods, other DataTables methods implemented in addRow() are .show(), .draw(imitation) and .node():
-
row.add together()adds a new row to the table using the given data. -
.draw()redraws and updates the table in the current context. -
.show()displays a field in our tabular array. This is useful for cases when yous desire to have actress form fields available, but simply show them nether sure weather. -
.draw(fake)adds a new row without resetting or distorting the electric current page. -
.node()serves equally an event listener, it returns the DOM chemical element for the requested field thus enabling DOM manipulation of the field.
We so take our addRow() method which we built and bind it to a button using jQuery'due south .click() method. When the button is clicked, addRow() automatically executes its functions on our table.
$ ( '#add' ) . on ( 'click' , this . addRow . bind ( this , dataTable) ) ; 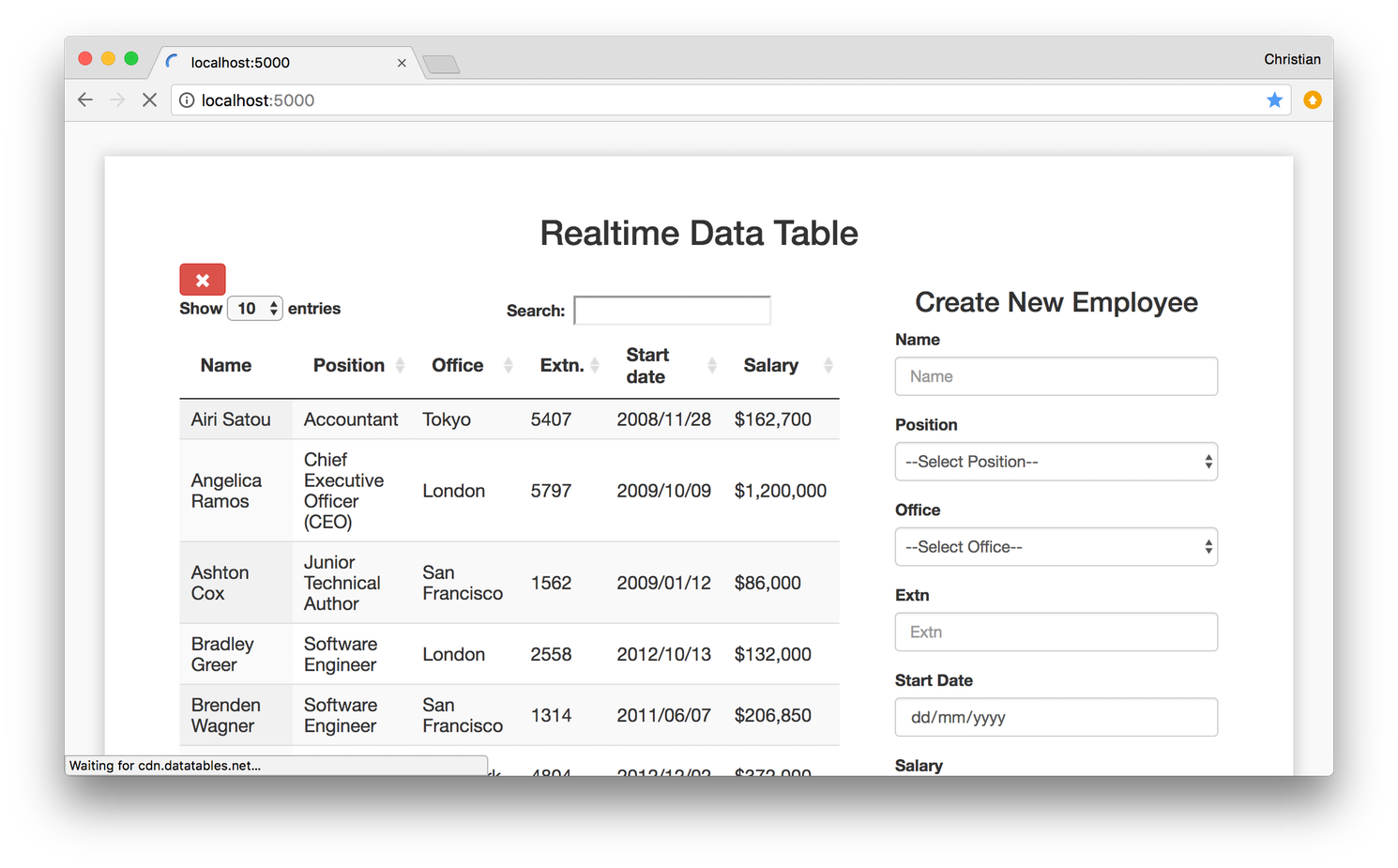
Selecting and removing existing records from table
Permit'south at present create a method called selectRow() , its function is to select a row in our table. Selecting a row puts the row to the spot so nosotros tin can be able to remove information technology. The method just adds a selected class to the selected row and removes any other row that selected class was previously added to:
selectRow ( dataTable ) { if ( $ ( this ) . hasClass ( 'selected' ) ) { $ ( this ) . removeClass ( 'selected' ) ; } else { dataTable. $ ( 'tr.selected' ) . removeClass ( 'selected' ) ; $ ( this ) . addClass ( 'selected' ) ; } } 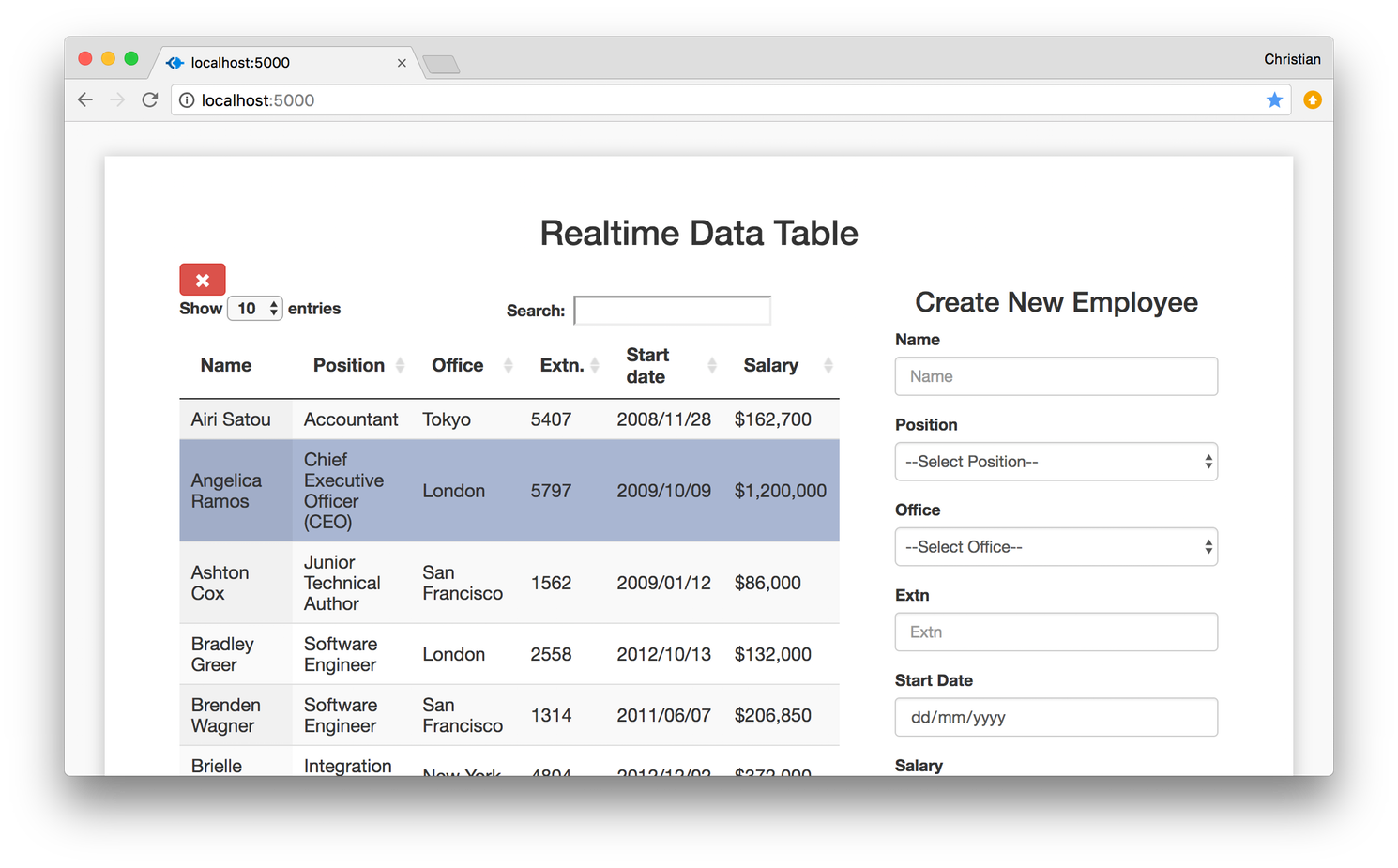
Nosotros also create a method called removeRow() , its part is to remove a row from our tabular array. The row removed is the row with the selected class:
removeRow ( dataTable ) { dataTable. row ( '.selected' ) . remove ( ) . draw ( simulated ) ; } We then proceed to demark selectRow() and removeRow() to their respective result triggers using jQuery'due south .click() method equally nosotros did previously with addRow().
const self = this ; $ ( '#realtime tbody' ) . on ( 'click' , 'tr' , function ( ) { self. selectRow . bind ( this , dataTable) ( ) ; } ) ; $ ( '#remove' ) . on ( 'click' , this . removeRow . bind ( this , dataTable) ) ; Realtime updates with Pusher
To enable realtime updates on our table, we will integrate Pusher Channels. Channels is a unproblematic hosted API for quickly, easily and securely implementing realtime 2-manner functionality on spider web and mobile apps. To achieve this, Pusher is to be installed both on the client side and on the server side. The client side is with the <script> tag while nosotros npm install on the server side. A couple of frameworks and packages will exist integrated alongside Pusher, these are:
- Express: A fast, lightweight, flexible framework for Node.js.
- bodyParser: A module that provides middle ware for extracting the unabridged body portion of an incoming request stream and exposes it on
req.bodyas something easier to interface with. - cors: A Node.js package that provides middleware that can exist used to enable cantankerous-origin resources sharing with different options.
- Axios: A hope based HTTP client for JavaScript mainly used to ship asynchronous HTTP requests to REST endpoints and perform CRUD operations.
Installing Pusher on the Client
Nosotros brainstorm by including the Pusher Client library and Axios on our HTML page:
<body > <script src = "https://js.pusher.com/4.1/pusher.min.js" > </script > <script src = "https://cdnjs.cloudflare.com/ajax/libs/axios/0.16.2/axios.js" > </script > </body > In our script.js file, nosotros create a method called sendToServer() where we perform a Postal service request with Axios. Nosotros pass in two parameters in our Mail request; the first is the URI of our service endpoint and the second is our table data which nosotros gear up equally a value to a newly created constant which nosotros call formData
sendToServer ( ) { const formData = this . buildForm ( ) ; axios. post ( 'http://localhost:2000/record' , formData) . and so ( response => console. log (response) ) ; } We and so institute our connection with Pusher by creating a new Pusher example.
In our instance, nosotros insert the free API key we get when signing upwards with Pusher. To ensure connection traffic is encrypted, nosotros set encrypted to the Boolean true in our app.
var pusher = new Pusher ( 'APP-KEY' , { cluster: 'CLUSTER' , encrypted: true } ) ; The central is function of the credentials that are generated when a new Channels app is created from your Pusher dashboard. You tin create an account by signing up. Come across Appendix at the finish of the article to learn how to setup a Pusher account.
Installing Pusher Channels on the Server
Starting time, run the post-obit command to install the server dependencies:
npm install express body-parser cors A server.js file is created; we then initialize Express later on which we configure Express to support cantankerous-origin resource sharing, encoded body and JSON. Nosotros then create a new Pusher instance which has an object containing our app ID, cardinal, secret, cluster, and encryption preference.
Next, nosotros create a POST route and in it we use Pusher to trigger an upshot named new-record through a tape channel.
const express = require ( 'express' ) ; const bodyParser = crave ( 'body-parser' ) const Pusher = require ( 'pusher' ) const cors = require ( 'cors' ) const app = limited ( ) ; app. use ( cors ( ) ) app. apply (bodyParser. urlencoded ( { extended: false } ) ) app. use (bodyParser. json ( ) ) const pusher = new Pusher ( { appId: 'APP-ID' , key: 'Central' , secret: 'SECRET' , cluster: 'CLUSTER' , encrypted: true } ) ; app. post ( '/record' , ( req, res ) => { console. log (req.body) ; pusher. trigger ( 'records' , 'new-tape' , req.body) ; res. transport ( 'Pushed' ) ; } ) app. mind ( 2000 , ( ) => console. log ( 'Listening at 2000' ) ) ; To get realtime updates on our tabular array, in our script.js file (client side) we use Pusher'southward subscribe() method to subscribe to our channel records. We then define a callback function that binds our upshot new-record and with it, our data.
var pusher = new Pusher ( 'APP-Central' , { cluster: 'CLUSTER' , encrypted: true } ) ; var channel = pusher. subscribe ( 'records' ) ; channel . bind ( 'new-record' , ( information ) => { this . addRow (dataTable, data) ; } ) ; 
Decision
With this walk through, you should be able to build cross platform realtime apps with ease. Other DataTables and Pusher features are available but their utilize depends on the requirements of your app. You can take a expect at the DataTables documentation and while yous're at information technology, take a glance at Pusher'south as well. For a deeper comprehension of the projection, feel free to explore further on GitHub.
Appendix: Pusher Channels Setup
- Sign up for a gratis Pusher business relationship:
- Create a new Channels app by selecting Apps on the sidebar and clicking Create New button on the bottom of the sidebar:
- Configure an app past providing bones information requested in the grade presented. You tin can also choose the surround y'all intend to integrate Pusher with for a better setup experience:
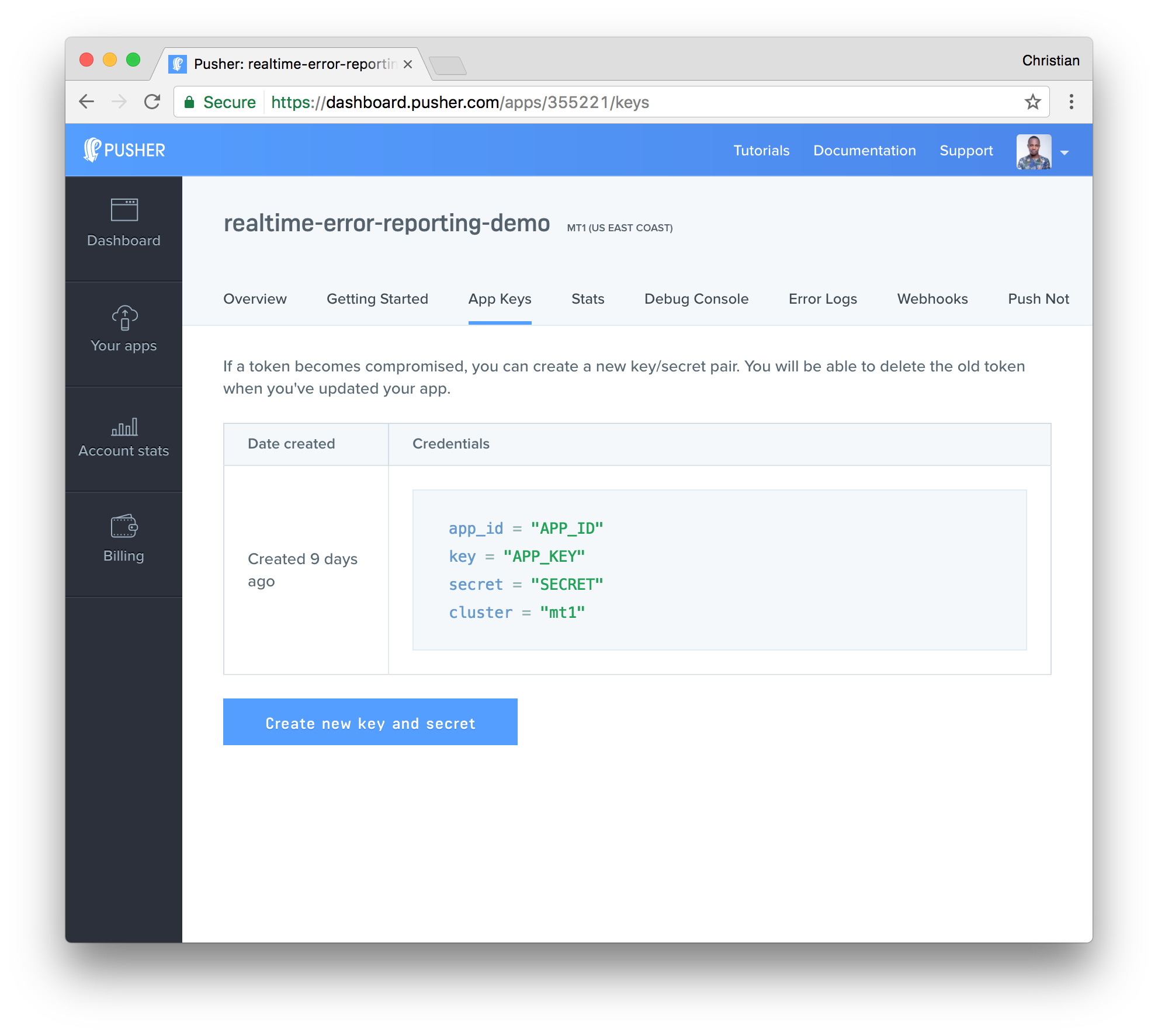
- You can call back your keys from the App Keys tab:
How To Update A Table Based On A Selection Javascript,
Source: https://pusher.com/tutorials/realtime-table-datatables/
Posted by: robinsonhans1996.blogspot.com


0 Response to "How To Update A Table Based On A Selection Javascript"
Post a Comment